explain both the positive and negative arguments of rfid tagging Implementation considerations collectively represent a critical disadvantage of RFID. The material and capability requirements are more complex than systems based on barcodes and optical . See more $7.99
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · schneider rfid problems
2 · rfid vs aidc
3 · rfid system advantages and disadvantages
4 · radio frequency rfid advantages
5 · pros and cons of rfid
6 · disadvantages of rfid technology
7 · advantages of rfid
Not possible, doesn’t matter what kind of access card you have, the readers won’t read the .
what is rfid technology
Radio frequency identification is an automatic ID system. Like a barcode or the magnetic strip .
schneider rfid problems
A specific RFID system fundamentally consists of a small radio transponder, a radio receiver, and a radio transmitter. An electromagnetic pulse from an RFID reader activates a nearby tag. In turn, the activated tag transmits digital data back to the reader. The . See moreImplementation considerations collectively represent a critical disadvantage of RFID. The material and capability requirements are more complex than systems based on barcodes and optical . See more
The advantages of RFID collectively center on its superiority over barcoding. In general, the technology provides benefits and applications that are not present from an identification and . See moreThere are two types of RFID tags as follows. 1. Passive tags (no internal power source, .There are basically three types of RFID tags that are commonly used: active, passive, and .
Tags are application specific. No one tag fits all. Possibility of unauthorized reading of passports and credit cards. More than one tag can respond at the same time. Disadvantages of RFID in more detail. RFID systems are often more expensive than barcode systems.
What is RFID? RFID refers to Radio Frequency Identification. It is a modern .Radio frequency identification is an automatic ID system. Like a barcode or the magnetic strip on a credit card, an RFID tag provides a unique identification code that can be read by a scanning device. Unlike other ID systems, RFID uses radio waves to communicate with readers.
rfid vs aidc
rfid system advantages and disadvantages
sssd smart card features
There are two types of RFID tags as follows. 1. Passive tags (no internal power source, powered by the reader’s signal) 2. Active tags (powered by an internal battery and can transmit signals on their own). • RFID Reader: The reader emits radio waves through its antenna to power the passive RFID tag or to communicate with an active tag.
Tags are application specific. No one tag fits all. Possibility of unauthorized reading of passports and credit cards. More than one tag can respond at the same time. Disadvantages of RFID in more detail. RFID systems are often more expensive than barcode systems.
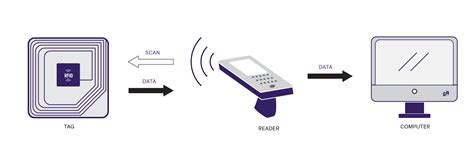
Explore the pros and cons of QR codes, NFC, RFID, and GPS tags for asset tagging. Discover which technology suits your asset management needs best. At a simple level, RFID systems consist of three components: an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator).
There are basically three types of RFID tags that are commonly used: active, passive, and semi-passive. An active tag comprises a transmitter and a power source (typically a battery) which is used to power the microchip’s circuitry as well as for broadcasting the signal to a reader. An electromagnetic pulse from an RFID reader activates a nearby tag. In turn, the activated tag transmits digital data back to the reader. The technology is somewhat similar to barcoding. Both involve ascribing unique numbers or data into an object for it to become identifiable and trackable.
Control Theft: RFID adds a whole new level of visibility to the supply chain by being able to accurately identify when goods leave one location and enter the next (i.e., a receiving dock, employee parking lot, etc.) Honeywell RFID Smart labels offer a broad selection of products suitable for a wide range of applications.RFIDs can replace barcode tags and identify an animal's herd of origin. Automatic toll collection. Perhaps the most common way RFIDs are currently used, the tags allow tolls to be debited from a prepaid account when vehicles drive by. The Smart Key/Smart Start option for some vehicles.Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs.
Radio frequency identification is an automatic ID system. Like a barcode or the magnetic strip on a credit card, an RFID tag provides a unique identification code that can be read by a scanning device. Unlike other ID systems, RFID uses radio waves to communicate with readers.There are two types of RFID tags as follows. 1. Passive tags (no internal power source, powered by the reader’s signal) 2. Active tags (powered by an internal battery and can transmit signals on their own). • RFID Reader: The reader emits radio waves through its antenna to power the passive RFID tag or to communicate with an active tag.Tags are application specific. No one tag fits all. Possibility of unauthorized reading of passports and credit cards. More than one tag can respond at the same time. Disadvantages of RFID in more detail. RFID systems are often more expensive than barcode systems.
Explore the pros and cons of QR codes, NFC, RFID, and GPS tags for asset tagging. Discover which technology suits your asset management needs best. At a simple level, RFID systems consist of three components: an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator).There are basically three types of RFID tags that are commonly used: active, passive, and semi-passive. An active tag comprises a transmitter and a power source (typically a battery) which is used to power the microchip’s circuitry as well as for broadcasting the signal to a reader.
An electromagnetic pulse from an RFID reader activates a nearby tag. In turn, the activated tag transmits digital data back to the reader. The technology is somewhat similar to barcoding. Both involve ascribing unique numbers or data into an object for it to become identifiable and trackable.
Control Theft: RFID adds a whole new level of visibility to the supply chain by being able to accurately identify when goods leave one location and enter the next (i.e., a receiving dock, employee parking lot, etc.) Honeywell RFID Smart labels offer a broad selection of products suitable for a wide range of applications.
RFIDs can replace barcode tags and identify an animal's herd of origin. Automatic toll collection. Perhaps the most common way RFIDs are currently used, the tags allow tolls to be debited from a prepaid account when vehicles drive by. The Smart Key/Smart Start option for some vehicles.
radio frequency rfid advantages
pros and cons of rfid
NFC Cards On-Metal NFC . PVC Cards with 125 kHz Q5 RFID Chip by HID. Quick view. View .
explain both the positive and negative arguments of rfid tagging|rfid vs aidc